Who’s Really Winning Putin’s War?
Editor’s Note: With the markets struggling in 2022, we feel this urgent guest editorial is important to share with you. The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine is having a major impact on the world economy – particularly in the energy sector. My colleague Matt Benjamin at The Oxford Club has the details on how that could affect natural gas prices going forward.
Plus, our friend Alexander Green, the Club’s Chief Investment Strategist, recently sat down with journalist Bob Paff to discuss Vladimir Putin’s decision to cut off natural gas supplies to Europe.
Click here to see why that could be a major mistake and how you could profit as a result.
– Ryan Fitzwater, Associate Publisher
Wars change things. Sometimes radically.
The world wars of the 20th century redrew the global map, dissolved old empires and created new nations out of old ones.
Regional, more limited wars also bring changes. It can be argued that the Vietnam War altered American culture and politics in profound and lasting ways.
The current war in Ukraine is no exception. It certainly resurrected the Cold War between Russia and the West (which many people believed ended when the Soviet Union collapsed). It is also likely to affect politics in Europe and the United States as politicians take sides on supporting the Ukraine war effort.
Perhaps most immediately, the Russia-Ukraine conflict is scrambling energy consumption, supply and policy across Europe and in other nations around the globe.
That will have major repercussions for global energy markets and investors going forward, perhaps permanently.
It may even present new opportunities for investors (more on that below).
It’s a Gas, Gas, Gas
Natural gas is Europe’s largest energy source – bigger than crude oil and coal.
In 2021, Europe received 45% of its natural gas from Russia… and some countries on the continent are even more dependent on Russian gas.
Germany – Europe’s largest economy – gets 55% of its gas from Russia. That gas heats Germany’s homes and powers its mighty manufacturing sector. In those two areas, gas is nearly 40% of the total energy mix.
After Russia invaded Ukraine, Germany halted one gas pipeline from Russia as punishment. Russia retaliated by reducing gas flows to Germany. Now Germany has announced plans to replace all Russian gas imports by mid-2024.
Germany isn’t alone. The broader European Union plans to replace two-thirds of Russian gas imports as soon as the end of this year.
Yet as winter approaches, European nations are scrambling to find those replacements.
The majority of them will be in the form of liquefied natural gas (LNG). Natural gas can be liquefied and loaded onto ships. Once it arrives at European ports, it is regasified and moved into local pipelines.
Europe is already the largest LNG importer in the world. And because of the conflict in Ukraine, it’s suddenly poised to import much more.
Yet there are bottlenecks in importing LNG. There are simply not enough regasification facilities on the continent to process all of the LNG imports needed to replace Russian supplies.
Concerns about supply have driven the price of natural gas in Europe up about 35% over October 2021’s price.
And spiking demand for LNG has caused a shortage of tankers, which has pushed shipping rates for LNG to record levels.
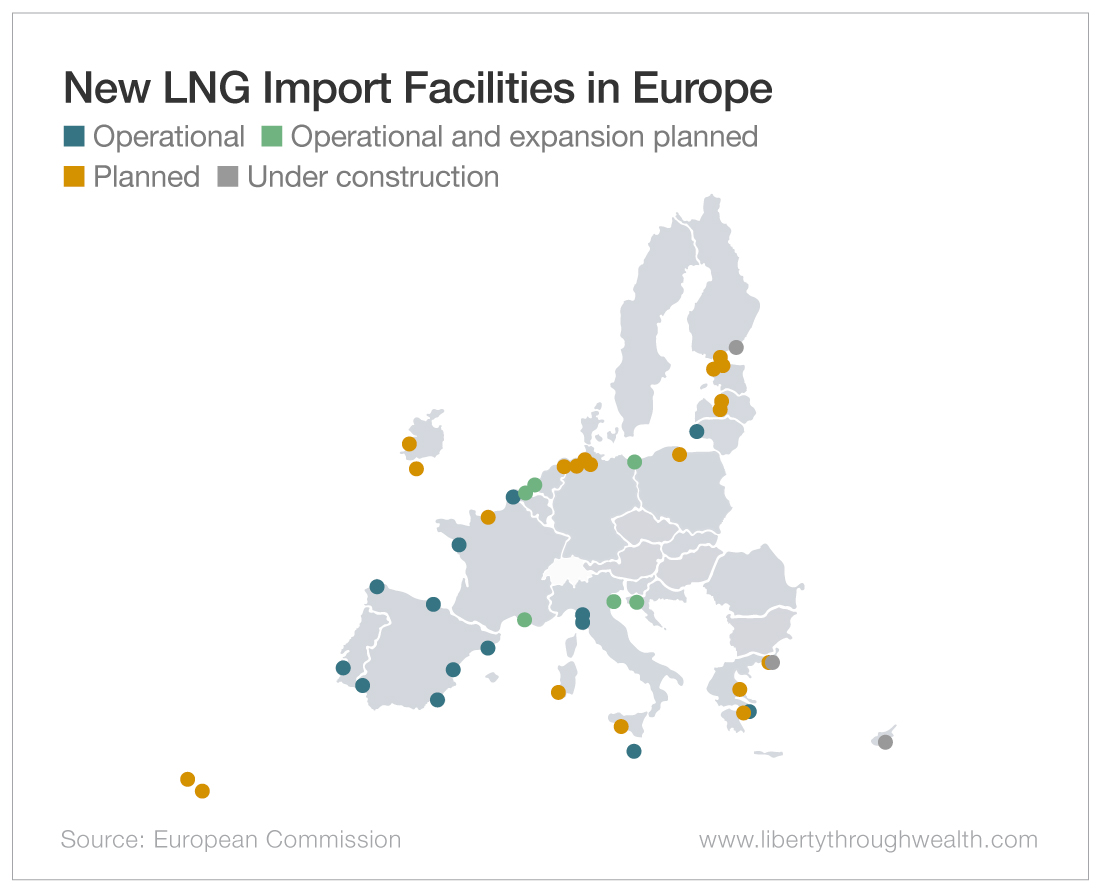
Thus there is now a scramble to create new facilities. The quickest way to do that is through floating storage regasification units, or FSRUs. These can be built much more quickly than permanent onshore import terminals.
As a result, there is a flurry of FSRU construction going on right now, with some 25 new FSRUs expected to be completed within a couple of years – the first of them by the end of this year. Those 25 FSRUs include five in Germany (plus two onshore LNG import sites), five in Greece, two in the Netherlands, four in Italy and two in Ireland.
France, Finland, Estonia, Cyprus and Poland also have plans for new FSRUs.
Who’s Got Gas?
And where will all that LNG come from?
Today the United States is the world’s largest producer of natural gas. It produced over 934 billion cubic meters last year, well above Russia’s 702 billion cubic meters.
In addition, in the first quarter of this year, the U.S. became the largest exporter of LNG, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
So Europe will lean heavily on imports of U.S. LNG.
As I wrote above, this is not a temporary shift in energy markets. Europeans were taken by surprise by the Russian invasion of Ukraine. They were terrified to find out how dependent they were on Russian energy.
And they’ve become determined to never again be so vulnerable to the whims of a dictator like Vladimir Putin.
That’s good news (eventually) for Europeans. And it’s great news for U.S. natural gas suppliers and shippers… as well as for investors who know which of those companies will best take advantage.
Your Action Plan: In fact, Oxford Club Chief Investment Strategist Alexander Green has his sights set on a special opportunity that could make early investors a fortune.
He recently sat down with journalist Bob Paff to discuss the company he believes is poised to make shareholders a killing.
Invest wisely,
Matt
Fun Fact Friday
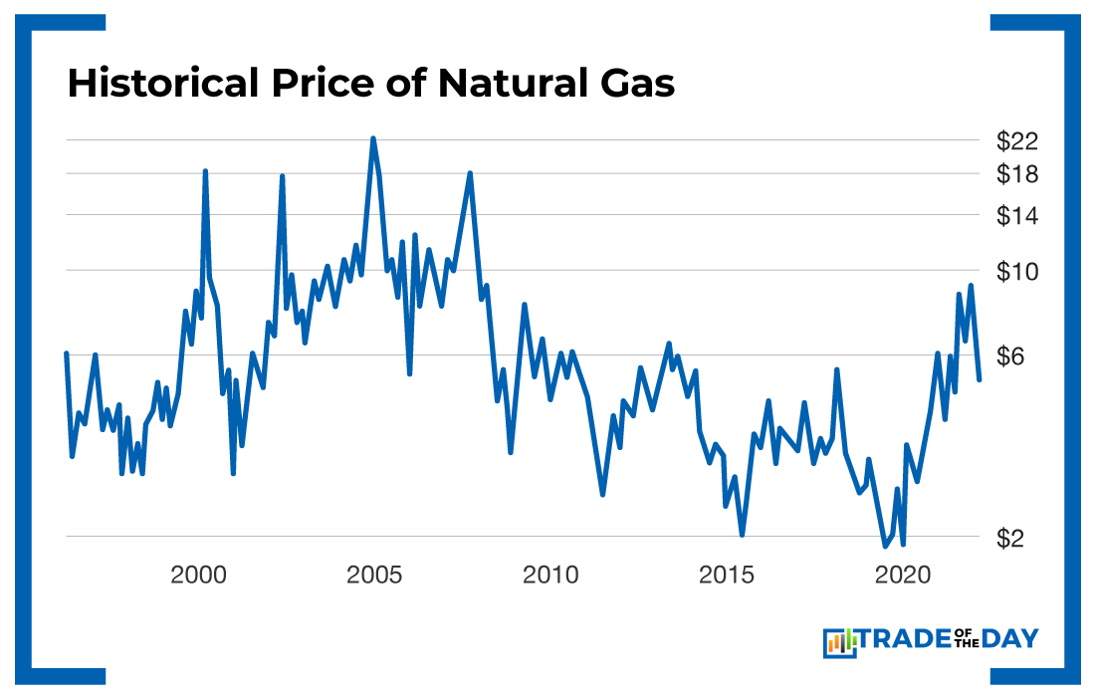
Energy prices have been a major sticking point in the world economy in 2022. Here’s a look at the historical price of natural gas. The current price as of October 25, 2022, is $5.17.
Recently, Russia cut off all gas supplies through the Nord Stream 1 pipeline to Europe. This is no small thing – and European energy prices have spiraled out of control as a result.
See why Alexander Green thinks this move is going to cost Vladimir Putin dearly.
 |
More from Trade of the Day
The No. 1 Insider Stock for 2024?
Jul 26, 2024
Why I’m Buying This 3-month Trigger Catalyst
Jul 24, 2024
Jul 23, 2024